T1 2022: What’s New For Seniors

Taxpayers who turned 65 in 2022 will have some new tax filing nuances when preparing the 2022 tax return this spring. Here’s what you need to know:
Excerpt from Knowledge Bureau’s Advanced Tax Update Course
Old Age Security. The Old Age Security pension is a taxable monthly payment available to most Canadians aged 65 or older. Benefits are indexed to the cost of living.
For those who chose to start their OAS pension, the amounts received will be taxable and therefore reportable on the T1. Pensions received under this Act are shown in Box 18 of the taxpayer's Form T4A(OAS) Statement of Old Age Security and are included in income on line 11300.
Residents: Getting Started. Those who have been resident in Canada for their whole lives will receive a notice soon after their 64th birthday of their eligibility to receive the pension with an option to defer if they choose to do so. Those who do not receive such a letter should apply as soon as possible after their 64th birthday.
Newcomers to Canada may not qualify for this benefit until they have been resident in Canada for at least ten years. Those who have been resident in Canada for less than 40 years after turning 18 years of age may find that they do not qualify for the full OAS pension.
Non-residents. Those who have lived in Canada for at least 20 years after turning age 18 can receive OAS if they lived and worked in a country that has a social security agreement with Canada. Those who do not qualify under these rules and who live out of the country for more than six months after the month of departure will find their OAS will stop. It is also not possible to collect the GIS (Guaranteed Income Supplement) if outside of Canada for more than six months.
2022 Old Age Security Payments (assumes full eligibility)
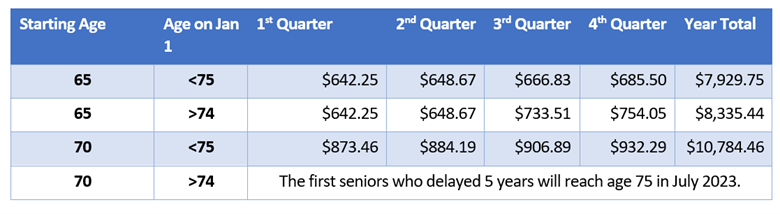
However, if net income is high, some of that OAS is repayable via the tax return. That’s a surprise to many who still work or draw larger pensions.
Clawbacks. Specifically, the OAS threshold base amount for 2022 is $81,761. Net income above this will result in an OAS clawback. When net income reaches $134,626, all of the standard OAS received is clawed back.
Note: Seniors who receive less than the standard OAS will have it all clawed back at a lower income level, and seniors who receive a larger OAS amount because they deferred starting the pension can have a higher net income before the benefits are fully clawed back.
The Social Benefits Repayment is deducted at line 23500 and added to taxes payable at line 42200.
Effect of Clawback on next payments receivable. For the following year, from July 1 to June 30, the taxpayer's Old Age Security payments are reduced each month by one-twelfth of the repayment payable. This amount is deemed to be income tax withheld and is reported as such on the taxpayer's T4A(OAS) Statement of Old Age Security for the next year.

Bottom Line: Understand your options to maximize the OAS by carefully crafting deductions to reduce your net income (if taxpayer has RRSP room and is under 72 or has a younger spouse, an RRSP contribution can help). Plus, it might make sense to defer the OAS altogether to receive more later.
Next Time: Should I Defer the OAS?
Evelyn Jacks is Founder and President of Knowledge Bureau, holds the RWM™, MFA ™, MFA-P™ and DFA-Tax Services Specialist designations and is the best-selling author of 55 books on tax filing, planning and family wealth management. Follow her on twitter @evelynjacks.
©Knowledge Bureau, Inc. All rights Reserved